List of Terms
ASCII:
- Acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange. A seven bit code standard adopted to facilitate data interchange between computers and operating systems. Primary input file format for parameters, precipitation, observed stage-discharge, and rating curves.
Baseflow:
- Streamflow which results from precipitation that infiltrates into the soil, eventually moving through the soil to the stream channel. This is also referred to as ground water flow, or dry-weather flow.
Basin:
- An area having a common outlet to which surface runoff flows.
BOP file:
- Acronym for Basin Overland Properties file. File extensions: *.bopx, *.bop. Vflo™ file containing the essential data that makes up a Vflo™ model, inluding information on the model domain, drainage network, channel and reservoir locations, model parameters, shapefiles, watch points, calibration factors, etc.
Calibration:
- The process of using historical data to estimate parameters in a hydrologic forecast technique.
Celerity:
- The kinematic wave celerity represents the velocity with which a wave propagates along a drainage network. The kinematic wave celerity within Vflo™ is represented as
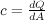 where Q is the discharge rate and A is the cross sectional area.
where Q is the discharge rate and A is the cross sectional area.
Hydrograph:
- Graph of discharge versus time.
Hyetograph:
- Graph of rainfall intensity or accumulation with time.
Infiltration:
- Movement of water from the surface into the soil. The rate of movement is controlled by the infiltration rate of the soil. Once the pore spaces in the soil profile have been filled, all rain that falls will runoff.
Prediction length:
- Establishes the duration (in hours) of flow prediction after rainfall has stopped. As large basins may have a delayed response, it is necessary to establish a prediction length greater than the rainfall interval to adequately represent the volume of streamflow produced.
Projection:
- Geographic coordinates in a plane referenced to the earth surface.
Radar:
- Acronym for Radio Detection and Ranging. Radar is a radio device or system for locating an object by means of ultrahigh-frequency radio waves reflected from the object and received, observed, and analyzed by the receiving part of the device in such a way that characteristics (such as distance and direction) of the object may be determined.
RRP file:
- Acronym for Rainfall Rate Properties file. Stores Vflo™ precipitation data, allowing runoff simulation, hydrograph generation, and flood prediction in Vflo™.
Vflo™ domain:
- Rectangular area defining the boundaries of the Vflo™ model. All parameter maps imported to Vflo™ must have the same domain.
Watershed:
- A drainage network defining an area of land that drains to a single outlet. Also referred to as a basin or catchment.
Z-R relationship:
- Z-R relationships are used to convert radar reflectivity observations (Z) to rainfall rates (R). Applying a Z-R relationship uses reflectivity data measured in decibels of reflectance, dBZ, to derive rainfall rates. Z-R relationships differ by the coefficients a and b used in the standard Z-R relationship, Z = aRb. The coefficient values are based on storm type and rain drop-size distribution.
